Civil Rights
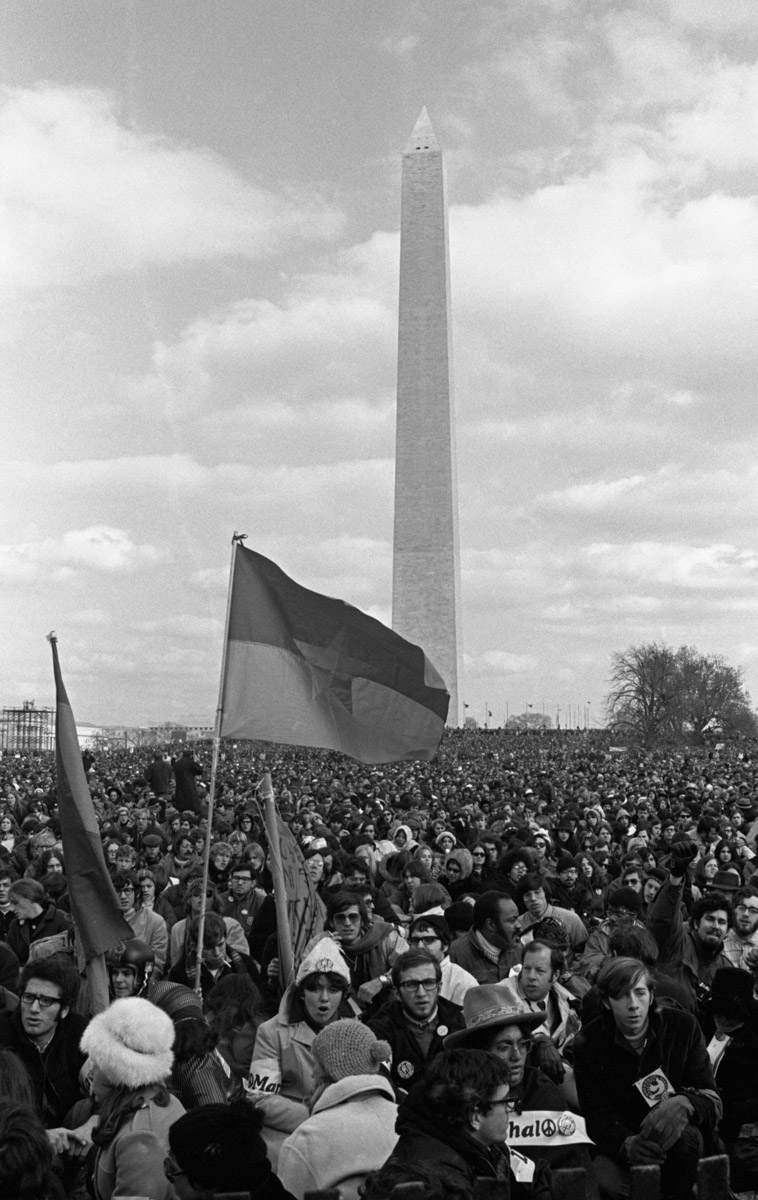
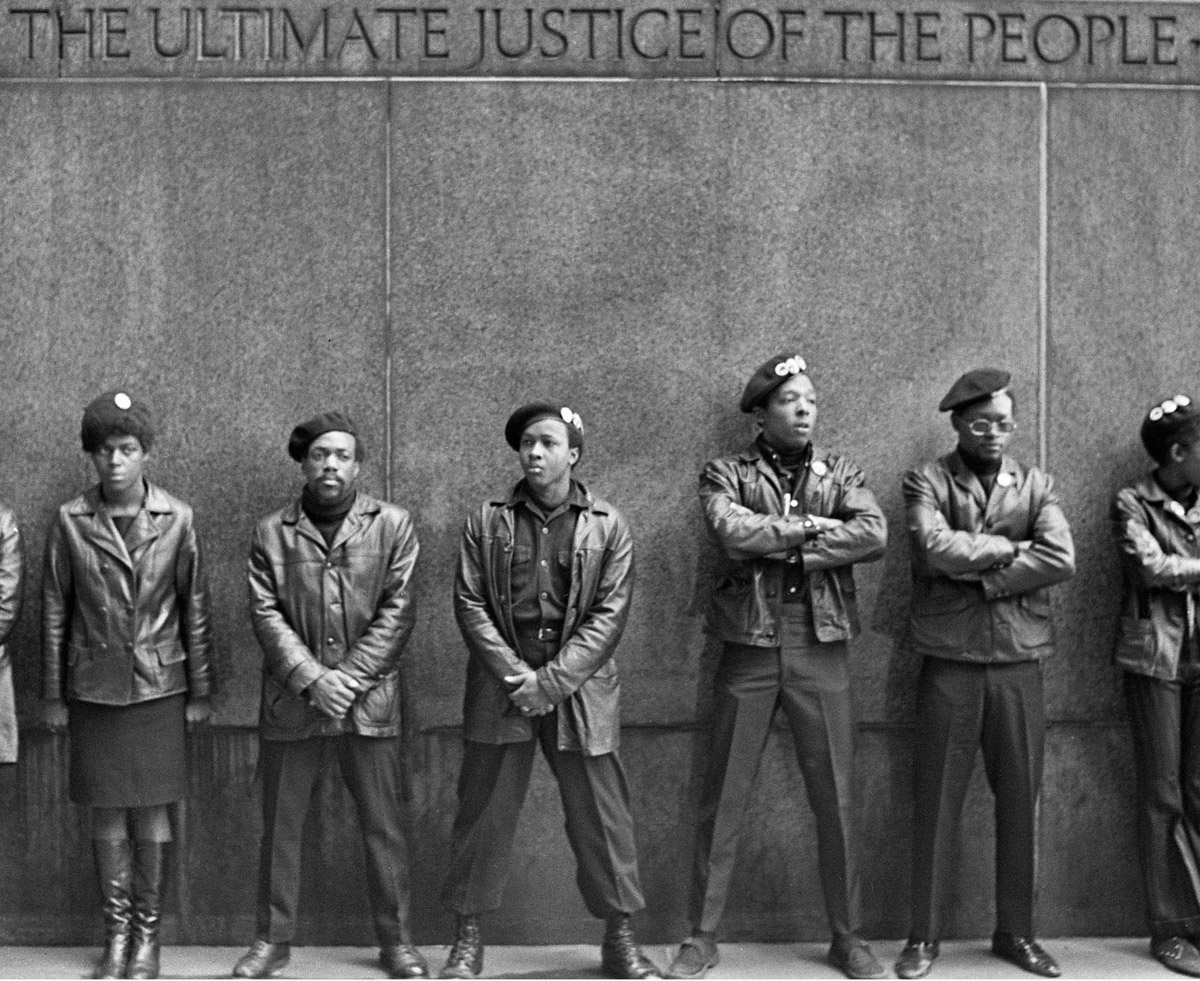
The civil rights movement was a mass popular movement to secure for African Americans equal access to and opportunities for the basic privileges and rights of U.S. citizenship. Although the roots of the movement go back to the 19th century, it peaked in the 1950s and 1960s. African American men and women, along with whites, organized and led the movement at national and local levels. They pursued their goals through legal means, negotiations, petitions, and nonviolent protest demonstrations (see pacifism and nonviolent movements). The civil rights movement was largest social movement of the 20th century in the United States. It influenced the modern women’s rights movement and the student movement of the 1960s.
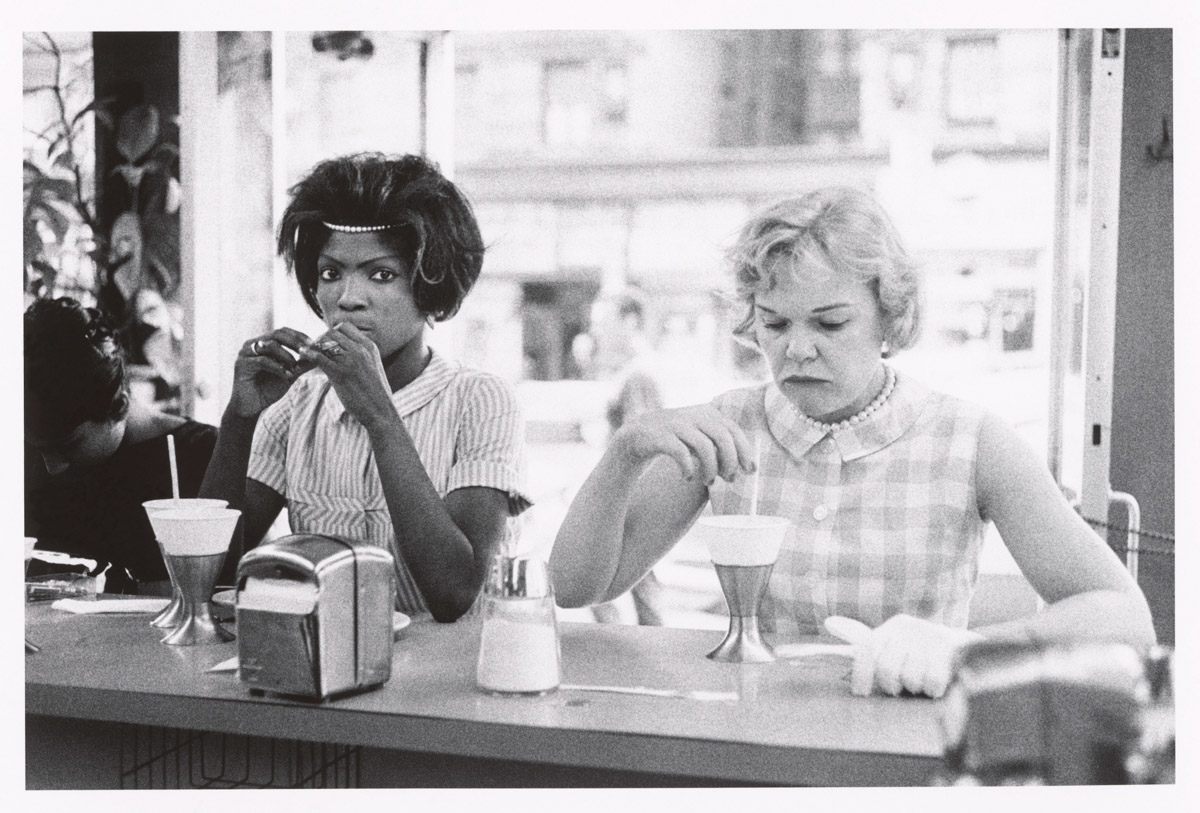
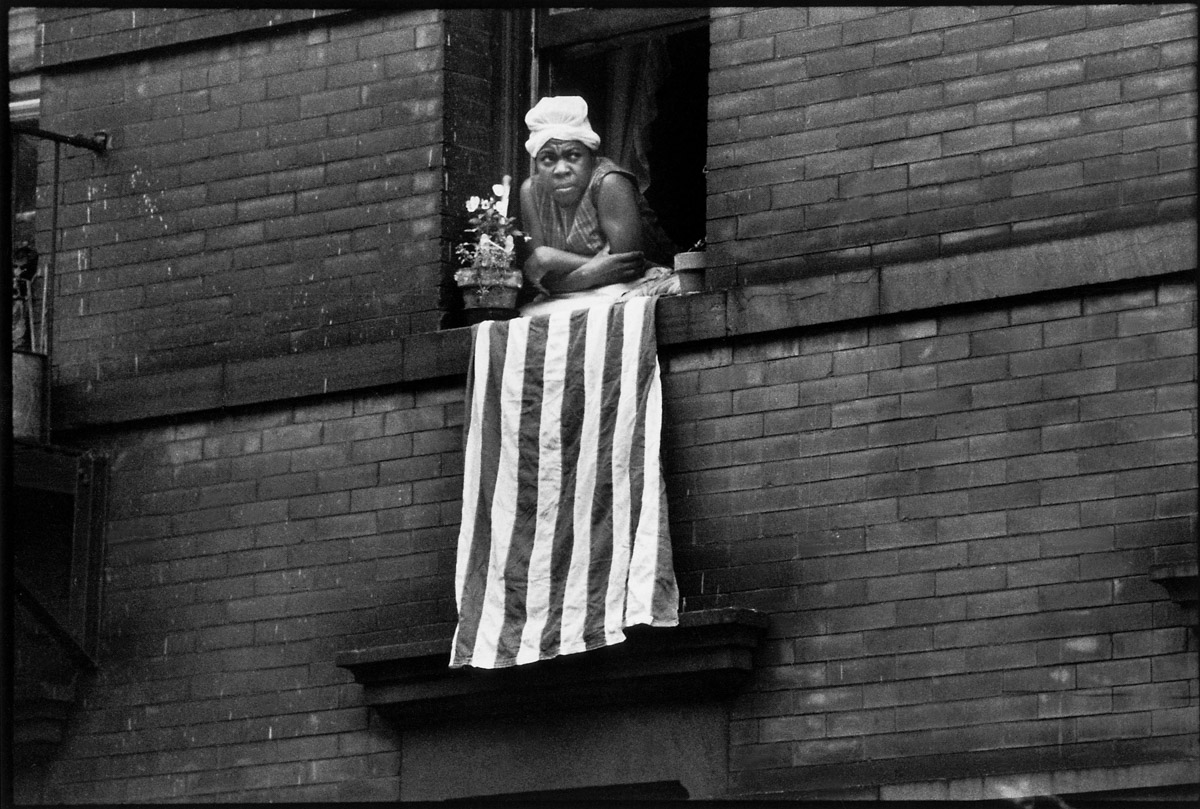
The civil rights movement centered on the American South. That was where the African American population was concentrated and where racial inequality in education, economic opportunity, and the political and legal processes was most blatant. Beginning in the late 19th century, state and local governments passed segregation laws, known as Jim Crow laws; they also imposed restrictions on voting qualifications that left the black population economically and politically powerless. The movement therefore addressed primarily three areas of discrimination: education, social segregation, and voting rights.